Cardiovascular disease is a major cause of mortality worldwide, and is directly related to the development of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) (Jiang et al, 2015). Globally, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death (World Health Organization, 2017). Within the 17.5 million individuals who die from CVDs, four out of five deaths are caused by heart attacks and strokes (World Health Organization, 2017). Approximately 30% of patients with ACS experience STEMI, which is associated with a 5–15% inhospital mortality rate (André et al, 2014; Vercellino, 2017: 2).
Platelet aggregation and subsequent formation of a thrombus are pertinent components of STEMI development, and this highlights the importance of pharmacological platelet inhibition in the treatment of this condition (Jiang et al, 2015; US Food and Drug Administration (USFDA), 2019).
At present, the optimal treatment for STEMI includes early administration of aspirin, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), a P2Y12 antagonist (ticagrelor, prasugrel or clopidogrel) and an anticoagulant (such as unfractionated heparin or enoxaparin), which is complemented by primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI) or fibrinolysis (Jiang et al, 2015; Chew et al, 2016; Sealy et al, 2020). Often these treatments are delivered through interdisciplinary partnerships between paramedics, physicians and interventional cardiologists (Khan et al, 2016; Johnson et al, 2015: 372–373).
Clopidogrel is the predominant P2Y12 receptor antagonist administered in STEMI management; it prevents platelet degranulation and, therefore, the inhibition of platelet aggregation. It is a second-generation P2Y12 receptor antagonist that actively impedes the binding of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to the platelets' surface receptors, preventing the subsequent activation of ADP-mediated glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (Johnson et al, 2015: 372; MIMSOnline, 2020). This prevents the inhibition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate driven calcium storage, increasing the upload of calcium into the platelet dense tubular system—a membrane system that plays a pivotal role in the modulation of platelet aggregation (Gerrard et al, 1978). This prevents platelet shape transformation and degranulation events that occur in blood clotting, and therefore inhibits platelet congregation and further formation of a thrombus in the patient with STEMI patient (Maynard, 2019).
Pharmacokinetically, the drug has a rapid absorption rate and can reach peak plasma levels, a mean of 3 mg/ml, from a 75 mg oral dose within 45 minutes of dosing (USFDA, 2019). The blood content is proportional to the Cmax (maximum concentration) linear gradient and the base measurement for this is a 300mg dose. There is no transient effect of clopidogrel, with the half-life duration lasting approximately 6 hours (USFDA, 2019).
As a prodrug, clopidogrel is absorbed through the gastrointestinal system, metabolised by the liver, experiences the first pass effect. It is transformed through two separate pathways, with one pathway where the drug is mediated by esterase and hydrolysed into an inactive carboxylic acid derivative (85%) (Karaźniewicz-Łada et al, 2014), and the other associated with cytochrome P450 (CYP2C19) enzymes (15%) (USFDA, 2019). Both pathways have the final result of turning the inactive metabolite into an active status, creating a thiol derivative (Jiang et al, 2015). It is the activated metabolite (clop-AM) that causes the antagonistic binding to the platelet receptors, inhibiting the assembly of thrombocytes for the remainder of the platelet's lifespan, which is approximately 5–10 days (USFDA, 2019; Karaźniewicz-Łada et al, 2014; Jiang et al, 2015).
Despite multiple studies and trials indicating its effectiveness, such as the CAPRIE (CAPRIE Steering Committee, 1996), CURE (Mehta et al, 2001), CLARITY (Sabatine et al, 2005), and COMMIT study (Bhala and Taggar, 2006), only a small number of statutory ambulance services in Australia and internationally have incorporated clopidogrel into their STEMI management regimens (Dhillon, 2015: 52; MIMSOnline, 2020).
The purpose of this report is to examine selected peer-reviewed articles and study trials relating to paramedic clopidogrel administration, and to determine whether there is a pharmacological basis—whether by way of safety, effectiveness or other related issues—that may be responsible for the decision by ambulance services to omit clopidogrel from their STEMI management regimens. After identifying potential key issues, the authors intend to form an opinion about whether this drug should be more widely used across international ambulance services.
Methods
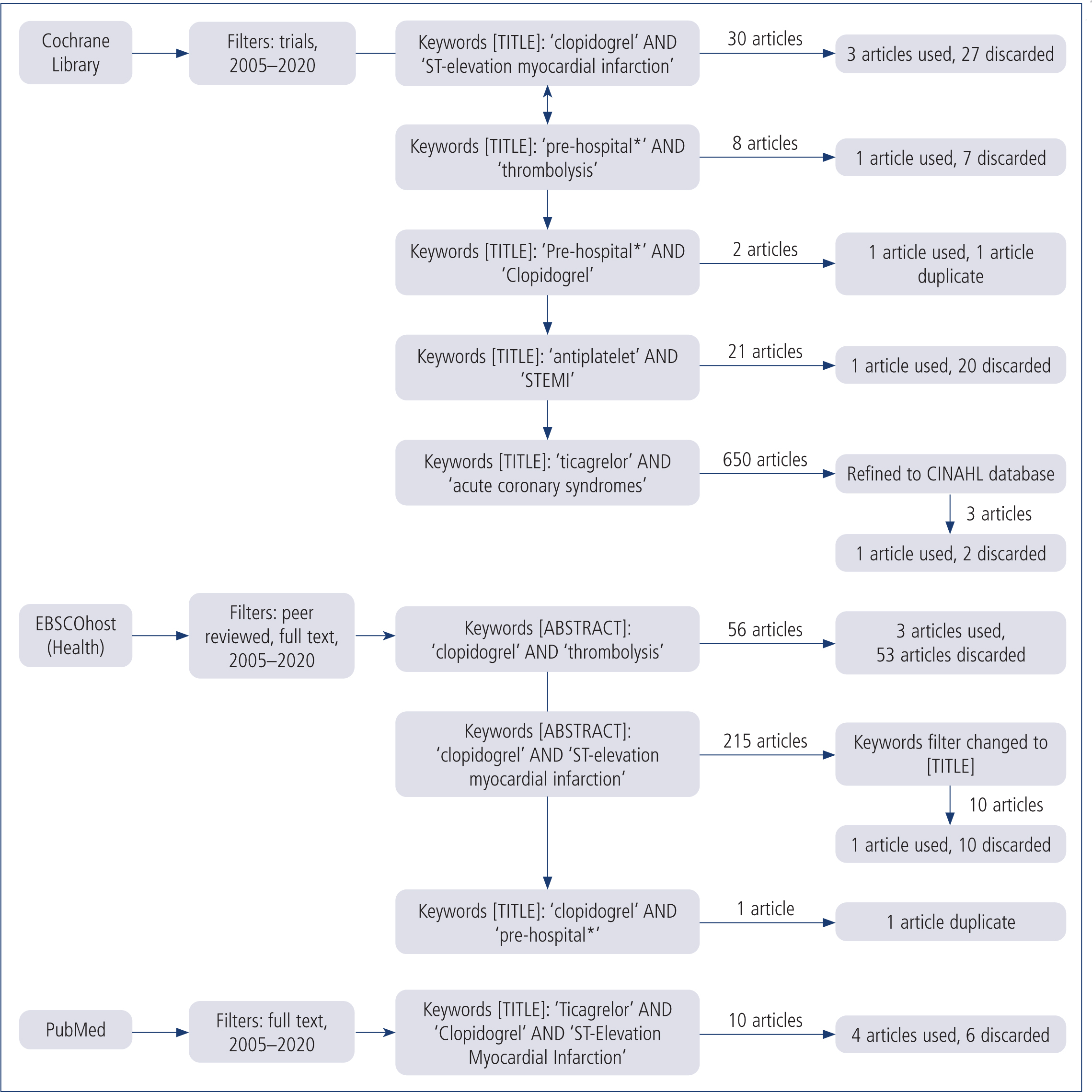
A combination of literature reviews and study trials were examined to investigate the appropriate use of clopidogrel in the prehospital environment. Documentation was collected from the EBSCOHost (Health) group of journal databases, PubMed, Scopus and the Cochrane Library using the primary search terms clopidogrel, pre-hospital*, ST-elevation myocardial infarction and antiplatelet. Secondary searches included ticagrelor, thrombolysis and acute coronary syndromes. The additional term ambulance was incorporated; however, it did not yield relevant content. The consistent filters assigned to each search were: full text; peer reviewed; and published between 2005 and 2020. Boolean operators were present to link keywords. Figure 1 shows the search method and results.
| Clopidogrel |
|
| Indications |
|
| Contraindications |
|
| Mechanism of action |
|
| Route of administration |
|
| Dose (adult) | Average doses across global ambulance services
|
| Adverse effects |
|
Duplicate articles were removed. Fourteen studies were relevant to this review with seven articles retained from the PubMed and EBSCOHost (Health) databases. All other articles and trials found during this search were deemed irrelevant to the topic.
Specific searches were conducted through international ambulance services websites to obtain the clinical practice guidelines relevant to clopidogrel and thrombolysis. Eight out of 12 ambulance services identified use clopidogrel within their thrombolysis regime for ACS (Table 2).
| International ambulance services | Clopidogrel use |
|---|---|
| New South Wales Ambulance | Yes |
| Queensland Ambulance Service | Yes |
| ACT Ambulance | No |
| Ambulance Tasmania | No |
| Ambulance Victoria | No |
| St John Northern Territory | Yes |
| St John Ambulance New Zealand | Yes |
| Wellington Free Ambulance | Yes |
| UK | Yes |
| Alberta Health Services | Yes |
| British Columbia Health Services | No |
| Ireland | Yes |
Results
The use of clopidogrel in the prehospital setting can be broken down into two components – safety and efficacy. Further segments specifically revolve around: bleeding tendency and risk; genetic responsiveness and metabolism; onset of effects; and the risk of secondary events such as MI, cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or mortality occurring, in comparison to other potential pharmacological regimens including ticagrelor or prasugrel.
Because the clotting cascade is automatically initiated by atherosclerotic thrombosis, platelet inhibition is essential, particularly in relation to bleeding risk (Ertaş and Tokgözoğlu, 2016: 900). The mechanism of clopidogrel involves binding to platelets, causing them to malfunction (MIMSOnline, 2020). This binding process is antagonistic and impairs platelets for the duration of their lifespan, resulting in an increased tendency to bleed (Dhillon, 2015).
Although bleeding tendency increases with clopidogrel use, particularly in conjunction with aspirin or other fibrinolytics (Oldgren, 2010: 1454-1456), there appears to be no significant increase in bleeding risk when doses are elevated (Ducci et al, 2013) or when it is used 2–8 days before a PCI (Zeymer et al, 2007).
The antagonistic nature of the drug alters and inhibits the function of other medications that use the P450 enzyme and cytochrome metabolism pathways, such as omeprazole, aspirin, heparin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (National Drug Agency, 2009: 19; Hasan et al, 2012). These medications competitively inhibit cytochrome P450/CYP2C19 enzyme activation and consequently reduce plasma concentrations of the active clop-AM. A concurrent use of these drugs has decreases drug efficacy and responsiveness overall, so reduces treatment quality (Hasan et al, 2012).
Clopidogrel has been deemed safe for use in relation to 12-month mortality rates and bleeding risks (Mehran et al, 2011; Khan et al, 2016). Secondary admissions after a cardiac event where the drug was used in the prehospital setting were found to be common practice, potentially because of the delayed onset of biochemical effects (Ducci et al, 2013). On the other hand, when clopidogrel was given in hospital rather than administered by paramedics, mortality rates were higher after 1 year (Oldgren et al, 2010). The P2Y12 trials also demonstrated that clopidogrel was associated with a relative reduction in death, recurrent MI or stroke (OR 0.80; 95% CI [0.72–0.90]; P<0.001), and a relative increase in extensive bleeding (OR 1.38; 95% CI [1.13–1.67]) (Chew et al, 2016). Long-term use of clopidogrel was associated with a reduction in mortality, secondary MI occurrences and CVAs (Zeymer et al, 2007).
With the onset of clopidogrel usually in a range of 30–60 minutes (MIMSOnline, 2020) because of its delayed metabolism by the liver (via oral administration), studies suggest that the antiplatelet effect of clopidogrel was insufficient when related to immediate hospital administration at a definitive care facility (Ducci et al, 2013). This effect is exacerbated by decreased circulatory issues that occur during STEMIs (Dhillon, 2015: 52; Vercellino et al, 2017: 2).
The paramedic Clopidogrel to Improve Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Acute Myocardial Infarction (CIPAMI) study also stated that clopidogrel did not increase the patency of the vessel when the period between administration and pPCI was less than 1 hour (Ducci et al, 2013: 4814). However, bleeding tendency did increase (Oldgren et al, 2010: 1454-1456). Both of these factors may become an issue, particularly in urban areas where transport time is reduced; however, a 600 mg dose administered as soon as possible was found to have greater effects over longer time periods (Biscaglia et al, 2013: 192; Ducci et al, 2013: 4814). Several studies conclude that, because of this, clopidogrel needs to be administered immediately after clinical indication or diagnosis to reach the therapeutic range at the appropriate intervals for effective treatment (Zeymer et al, 2007; Biscaglia et al, 2013; Vercellino et al, 2017).
| Author | Article title | Result | Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biscaglia et al, 2013 | Effects of pre-hospital clopidogrel administration on early and late residual platelet reactivity in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients undergoing primary intervention |
|
Clopidogrel needs to be administered as soon as possible when on scene for maximum effect because of its long half-life |
| Ducci et al, 2013 | Comparison of pre-hospital 600 mg or 900 mg vs peri-interventional 300 mg clopidogrel in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary coronary angioplasty. The Load&Go randomized trial |
|
Clopidogrel needs a longer time to take effect, regardless of dose. This would be an issue in urban areas where transport time is shorter |
| Dhillon, 2015 | Ticagrelor: a review of its use in adults with acute coronary syndromes |
|
Clopidogrel relies on the hepatic P450 enzymes for metabolism, leading to delayed onset of action, genetic polymorphism and higher variations in individual responses. The irreversible binding to receptors causes rapid offset and drug interactions |
| Vercellino et al, 2017 | Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in real-world patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction: 1 year results by propensity score analysis |
|
|
| Zeymer et al, 2007 | Efficacy and safety of clopidogrel 600 mg administered pre-hospitally to improve primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute myocardial infarction (CIPAMI): study rationale and design |
|
|
| Khan et al, 2016) | Pre-hospital thrombolysis in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a regional Australian experience | Clopidogrel was found to be safe to administer in the prehospital environment | Clopidogrel has fewer adverse effects and a higher safety range when given prehospitally |
| Zeymer et al, 2015 | Influence of morphine on the effect of clopidogrel and prasugrel in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction. Results of the ETAMI trial | Morphine adversely affects the antiplatelet inhibitory effects of clopidogrel | Morphine is often used in the treatment of ACS in ambulance protocols to treat associated pain |
| Bouman et al, 2010 | Predictive value of various platelet function tests on ST-segment resolution and clinical outcome in STEMI patients randomized to either dual or triple antiplatelet therapy: the OnTIME 2 platelet function substudy | The use of three different antiplatelets was more efficient than clopidogrel and aspirin alone | A combined antiplatelet treatment regimen has a more potent effect and is more beneficial in successful thrombolysis |
| Berwanger et al, 2018) | Ticagrelor vs clopidogrel after fibrinolytic therapy in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a randomized clinical trial |
|
Ticagrelor has a more predictable and consistent antiplatelet effect. Mortality rates are slightly lower with ticagrelor than clopidogrel but ticagrelor is associated with more adverse bleeding complications |
| Alfredsson et al, 2020 | Bleeding complications with clopidogrel or ticagrelor in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients–a real life cohort study of two treatment strategies |
|
Use in patients aged >75 years was unknown |
| Charpentier et al, 2020 | Bleeding risk of ticagrelor compared to clopidogrel in intensive care unit patients with acute coronary syndrome: a propensity-score matching analysis | Co-administration of ticagrelor/aspirin was associated with a greater bleeding risk than clopidogrel/aspirin | Combined antiplatelet therapy is effective when the appropriate medications are used. Ticagrelor/ASA has more complications than clopidogrel/ASA |
| Harding et al, 2017 | Contemporary antiplatelet therapy in acute coronary syndromes: are there differences in outcomes and discontinuation between clopidogrel and ticagrelor? |
|
Ticagrelor lacks consistent evidence as a take-home drug in comparison to clopidogrel, and is also associated with increased bleeding events |
| Hee et al, 2019 | Real-world use of ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in percutaneous coronary intervention-treated ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients: a single-center registry study |
|
Clopidogrel has less effect on patients with a lower bleeding risk, but has a greater effect with other patients |
| Tang et al, 2016 | Assessment of ticagrelor versus clopidogrel treatment in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention | Ticagrelor significantly reduced the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events and composite endpoints of non-fatal MI, stroke and cardiovascular death | There is no significant difference between ticagrelor or clopidogrel in relation to all-cause mortality, unplanned revascularisation, stent thrombosis, stroke, non-fatal MI or bleeding events |
The effectiveness of clopidogrel is affected by many factors that can delay onset, genetic responsiveness and metabolism, such as: genetic polymorphism, opioid use, vomiting and impaired gastrointestinal absorption, diminished circulatory ability during STEMI and concurrent use with other fibrinolytic medications (Vercellino et al, 2017). The metabolism of clopidogrel into its active form can be degraded by genetic variations in CYP2C19 enzymes, other medications that target CYP2C19 or variants of CYP450 enzymes (MIMSOnline, 2020). Patients exhibiting malfunction in the metabolism of these enzymes experience impaired effectiveness of platelet inhibition, leading to higher risk of cardiovascular events when dosages are not altered accordingly (MIMSOnline, 2020).
The Early Thienopyridine Treatment to Improve Primary PCI in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction’ (ETAMI) trial and Administration of Ticagrelor in the Cath-Laboratory or in the Ambulance for New ST-Segment–Elevation Myocardial Infarction to Open the Coronary Artery’ (ATLANTIC) study revealed that the use of morphine also affects the bioavailability of clopidogrel, resulting in an even longer time to onset (Dhillon, 2015: 64; Zeymer et al, 2015; Vercellino et al, 2017: 8).
Both Farag et al's (2018) and Frampton et al's (2020) review articles corroborate the information found in the ETAMI trial and ATLANTIC study. These research papers explain that the co-administration of morphine and oral P2Y12 platelet antagonists (i.e. clopidogrel) impairs the absorption rate and diminishes the onset and duration of the drug, subsequently weakening antiplatelet efficacy. These researchers concluded that the pharmacology of morphine negatively interacts with the mechanism of action of clopidogrel. This is because opioids have an inhibitory effect on gastric motility, which affects the absorption ability of the gastrointestinal system and decreases peak plasma levels of active metabolites within oral medications (Zeymer et al, 2015; Giannopoulos et al, 2016).
According to Hobl et al (2014), morphine diminishes the effects of a 600 mg dose of clopidogrel to a 300 mg dose, thereby increasing mortality. Hobl et al (2014: 633) also stated that ‘morphine causes a poor metaboliser phenotype in individuals genetically prone to extensively metabolised clopidogrel’. Although morphine is a commonly used analgesic in prehospital STEMI management, GTN or fentanyl could be considered to prevent this additional effect (Johnson et al, 2015: 373).
Justifiably, one could argue that fentanyl would have a similar if not an identical effect to morphine, as both medications are opioid analgesics. Evidence discourages the use of the synthetic analgesia, however, reporting that fentanyl also has potential clinical implications relating to decreased absorption rates and drug efficacy (Ibrahim et al, 2018; McEvoy et al, 2018). There is an ethical standpoint an individual must make here—is it morally correct to withhold opioid analgesia because of its ability to downgrade the aggregation inhibitory effect? Further research is still required in this area.
Queensland Ambulance Service (2020) is an example of a paramedical service that uses clopidogrel in conjunction with other medication, as preparation for additional STEMI therapies on hospital admission. Clopidogrel administered in conjunction with other therapy has been proved to be more effective than when given alone (Bouman et al, 2010; Alfredsson et al, 2020). The Clopidogrel as Adjunctive Reperfusion Therapy—Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (CLARITY-TIMI) 28 substudy demonstrated that management of STEMI with clopidogrel, fibrinolysis and heparin leads to reduced ischaemic times and increased reperfusion (Zeymer, 2007: 267). The Clopidogrel as Adjunctive Reperfusion Therapy (CLARITY) study further emphasised that fibrinolysis was improved when clopidogrel was used (Zeymer, 2007: 266). The ExTRACT-TIMI-25 study demonstrated that combining clopidogrel with enoxaparin was also beneficial (Arntz, 2008: 301).
Ticagrelor and prasugrel are two other platelet antagonists commonly used in antiplatelet treatment regimens. To fully assess whether clopidogrel should be incorporated into international STEMI management in the prehospital setting, comparisons must be drawn with these alternative pharmacological treatments.
Ticagrelor is an adenosine diphosphate (ADP) antagonist that reversibly binds to P2Y12 receptors at an allosteric site (Hermanides et al, 2018). Ticagrelor is commonly used in broad-spectrum ACS patients presenting in an intermediate to high risk category of STEMI or non-ST ACS (NSTEACS) (Chew et al, 2016).
Ticagrelor is known for its faster onset, its lower risk of additional ischaemic events, MI, CVA and mortality (OR 0.84; 95% CI [0.77–0.92]), and is more efficacious when used in conjunction with aspirin than with clopidogrel (Dhillon, 2015; Chew et al, 2016; Tang et al, 2016; Vercellino et al, 2017; Berwanger et al, 2018).
Compared with clopidogrel, Dhillon (2015) and Vercellino et al (2017) stated that ticagrelor was associated with lower bleeding risk, while Hee et al (2019) noted it was more efficient in patients with a pre-existing bleeding risk. However, Chew et al (2016) and Harding et al (2017) found the opposite to be the case (OR 1.25; 95% CI [1.03-1.53]).
Berwanger et al (2018) and Alfredsson et al (2020) discovered that minor bleeding and complications, in addition to higher thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) scores, were more common with the administration of ticagrelor. However, fatal bleeding rates were comparable between the two (Berwanger et al, 2018; Alfredsson et al; 2020). In terms of bleeding risk related to co-administration, Charpentier et al (2020) found that ticagrelor and aspirin increased bleeding significantly more than clopidogrel and aspirin. Ticagrelor was also associated with higher discontinuation rates because of adverse events related to increased bleeding, dyspnoea, ventricular pauses/bradyarrhythmia, and inappropriate consumption/chronic overuse (Harding et al, 2017).
Prasugrel is another P2Y12 antagonist that is metabolised into its active form by cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver (Chew et al, 2016). Prasugrel was found in the Trial to Assess Improvement in Therapeutic Outcomes by Optimizing Platelet Inhibition with Prasugrel—Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction to be more effective in decreasing the risk of additional ischaemic events, MI, CVA and mortality (9.9% versus 12.1%; P< 0.001) (Wiviott et al, 2007). These findings are concurred in the study conducted by Chew et al, (2016) (OR 0.81; 95% CI [73–0.91]); however, prasugrel was associated with an increased risk of bleeding (OR 1.32; 95% CI [1.03–1.68]), particularly in patients receiving coronary artery bypass grafts (Chew et al, 2016). In patients who were aged over 75 years, with previous cerebrovascular disease, below the weight of 60kg and with a medical history of transient ischaemic attacks or strokes, prasugrel has been found to be harmful.
Prasugrel was found to exceed clopidogrel in terms of platelet inhibition (Hermanides et al, 2018), and is particularly efficient when no previous P2Y12 antagonists have already been administered, particularly when PCI is indicated (Chew et al, 2016). In the context of PCI, prasugrel should be administered immediately (Chew et al, 2016).
Discussion
The risks and benefits of the administration of clopidogrel in the prehospital setting are still under examination, which may be why only a small number of statutory ambulance services include it in their clinical protocols.
As various trials show, clopidogrel significantly reduces mortality without increasing bleeding intensity significantly. The use of clopidogrel in the prehospital environment, although reasonably safe, effective and easily administered, is more beneficial over long periods; this lends support to the use of other drugs, such as ticagrelor when transport durations are shorter (Ducci et al, 2013: 4814–4816).
Studies indicate that, although clopidogrel is effective, particularly in conjunction with aspirin or other fibrinolytic medications, ticagrelor and prasugrel are more potent, predictable and suitable for recurrent events, resulting in better clinical outcomes (Chew et al, 2016). As a result, ticagrelor and prasugrel are recommended as the firstline treatment in pPCI (Chew et al, 2016) for STEMI patients in metropolitan and inner regional zones.
Clopidogrel is more commonly used in conjunction with fibrinolysis and when ticagrelor and prasugrel are contraindicated (Nickson, 2019). The present review endorses that clopidogrel is most beneficial where there is a long distance between the patient scene and the hospital, which makes it a preferable anticoagulant in outer regional, rural and remote sectors.
Some aspects of clopidogrel, such as its concurrent use with morphine and the effectiveness of administration by paramedics within the prehospital setting, require further research.
Conclusion
Research leans towards the ongoing use of clopidogrel in the prehospital environment as an effective antiplatelet pharmacological intervention. However, further comprehensive studies need to be conducted to determine which antiplatelet medication (i.e. clopidogrel, ticagrelor or prasugrel) is suitable and whether there is substantial benefit to the early administration of P2Y12 inhibitors in the prehospital setting for the ongoing management of STEMI (for both PCI and fibrinolysis).
The objective of this study, however, was to review the safety and efficacy of clopidogrel administration within the prehospital environment for the management of STEMI, and to examine whether this drug should be incorporated into ambulance services internationally.
Although the benefits of clopidogrel administration are unlikely to be realised in the prehospital setting, it is clear from this study that the early administration of clopidogrel, such as by paramedics, is required to optimise onset duration, without the risk of clinically significant bleeding or secondary events.
Clopidogrel within the prehospital setting should ideally be used in regional locations to support the ongoing care, interventions and recovery of the patient well after paramedics have transferred them to definitive care, particularly when complemented within a combination of therapies (e.g. enoxaparin, aspirin, fibrinolysis or PCI) in the management of STEMI.
